Data Type
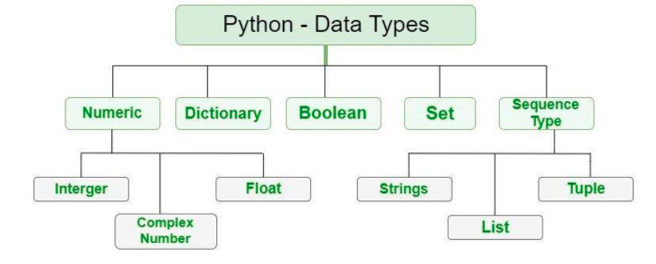
Data type represents the type of data a Variable or a Literal is referring to. Each data type has specific characteristics and operations associated with it. In Python, there are various data types, including number, string, boolean, list, tuple, and dictionary.
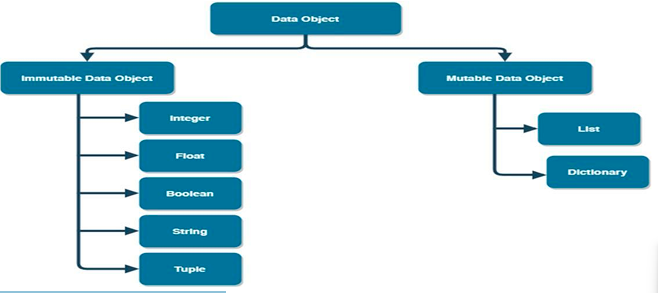
Mutable Objects
Mutable data objects are objects that can be changed after they are created. It is possible to add, remove, or modify elements within these data types. Example of mutable data types: List, Set and Dictionary.
Immutable Objects
An Objects whose values cannot be changed after they are created are called immutable objects. To change the value, a new object is created. Example of immutable data types: Number (Integer, Float), String, and Tuple.