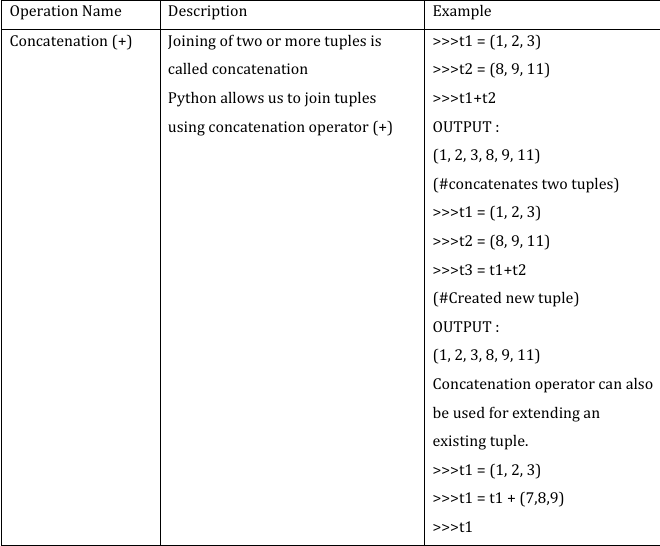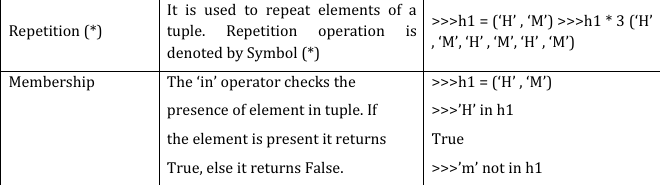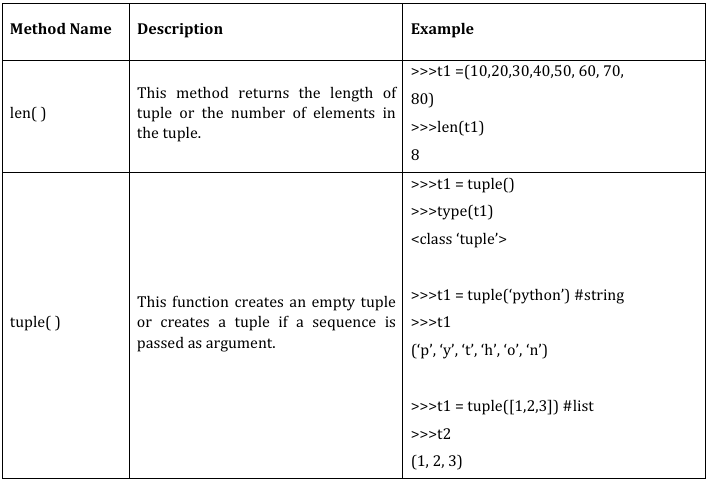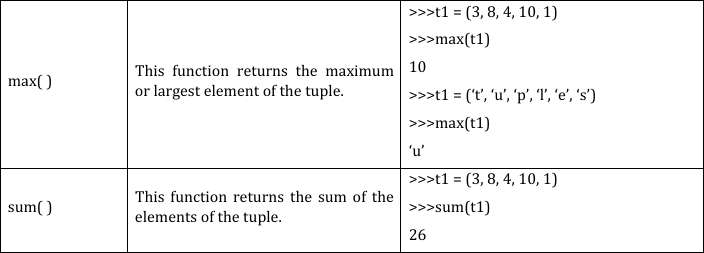
A tuple is a collection which is ordered and immutable (We cannot change elements of a tuple in place). Elements of a tuple are enclosed in parenthesis (round brackets) and are separated by commas. Tuples can store a sequence of values belonging to any type. Tuples allows duplicate members.
Ex:- T1 = ( ) # Empty Tuple
T2 = (4,5,6) # Tuple of integers
T3 = (1.5,4,9) # Tuple of numbers
T4 = ('x', 'y', 'z') # Tuple of characters
T5 = ('a',1.5,'KVS',45) # Tuple of mixed values
T6 = ('KVS', 'NVS', 'EMRS') # Tuple of strings
>>>t2 = (10,) # Single element tuple
>>>t3=(10,20,30,40,50) # Long tuple
>>>t4=(6,(4,5),9,7) # Nested Tuple
● tuple( ) function is used to create a tuple from other sequences.
● Indexing of tuple is similar to indexing of list.
● Difference between List and Tuple
A tuple means accessing and processing each element of it. A tuple can be traversed using a loop.
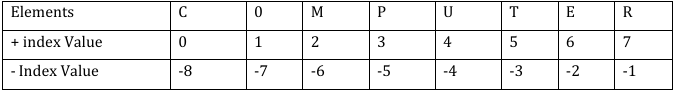
Ex:- >>> T1=(2,4,6,8,10)Elements of a tuple can be accessed using Indexing and Slicing, same as in string and list. if T1= ('C', 'O', 'M', 'P', 'U', 'T', 'E', 'R'):

>> T1[2] #WILL ACCESS 'M'
>>> T1[-3] #WILL ACCESS 'T'
>>> T1[1:7:1] #WILL ACCESS 'OMPUTE'